All the transforms functions currently supported by the DSP library.
This function computes a complex FFT from an input signal. It uses the Radix-4 "Decimate In Time" algorithm and does not perform a calculation "in place" which means that the input buffer has to be different from the output buffer.
Here is the formula of the FFT:
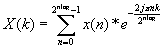
Relative functions:
This function computes a complex inverse FFT from an input signal. It uses the Radix-4 "Decimate In Time" algorithm and does not perform a calculation "in place" which means that the input buffer has to be different from the output buffer.
Here is the formula of the iFFT:
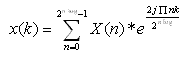
Relative functions:
This function computes a complex FFT from a real input signal. It uses the Radix-4 "Decimate In Time" algorithm and does not perform a calculation "in place" which means that the input buffer has to be different from the output buffer.
Here is the formula of the FFT:
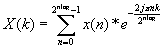
Relative functions:
Functions | |
| void | dsp16_trans_complexfft (dsp16_complex_t *vect1, dsp16_complex_t *vect2, int nlog) |
| 16-bit fixed point version of the complex FFT algorithm. More... | |
| void | dsp16_trans_complexifft (dsp16_complex_t *vect1, dsp16_complex_t *vect2, int nlog) |
| 16-bit fixed point version of the complex iFFT algorithm. More... | |
| void | dsp16_trans_realcomplexfft (dsp16_complex_t *vect1, dsp16_t *vect2, int nlog) |
| 16-bit fixed point version of the real to complex FFT algorithm. More... | |
| void | dsp32_trans_realcomplexfft (dsp32_complex_t *vect1, dsp32_t *vect2, int nlog) |
| 32-bit fixed point version of the real to complex FFT algorithm. More... | |
| void dsp16_trans_complexfft | ( | dsp16_complex_t * | vect1, |
| dsp16_complex_t * | vect2, | ||
| int | nlog | ||
| ) |
16-bit fixed point version of the complex FFT algorithm.
| vect1 | A pointer on a 16-bit complex vector which is the output buffer of this function. |
| vect2 | A pointer on a 16-bit complex vector which is the input buffer of this function. |
| nlog | It is the base-2-logarithm of the size of the input/output vector. Due to its implementation, this function computes only 4^n-point complex FFT. Therefore, the nlog argument has to be even. |
| void dsp16_trans_complexifft | ( | dsp16_complex_t * | vect1, |
| dsp16_complex_t * | vect2, | ||
| int | nlog | ||
| ) |
16-bit fixed point version of the complex iFFT algorithm.
| vect1 | A pointer on a 16-bit complex vector which is the output buffer of this function. |
| vect2 | A pointer on a 16-bit complex vector which is the input buffer of this function. |
| nlog | It is the base-2-logarithm of the size of the input/output vector. Due to its implementation, this function computes only 4^n-point complex iFFT. Therefore, the nlog argument has to be even. |
| void dsp16_trans_realcomplexfft | ( | dsp16_complex_t * | vect1, |
| dsp16_t * | vect2, | ||
| int | nlog | ||
| ) |
16-bit fixed point version of the real to complex FFT algorithm.
| vect1 | A pointer on a 16-bit complex vector which is the output buffer of this function. |
| vect2 | A pointer on a 16-bit real vector which is the input buffer of this function. |
| nlog | It is the base-2-logarithm of the size of the input/output vector. Due to its implementation, this function computes only 4^n-point complex FFT. Therefore, the nlog argument has to be even. |
| void dsp32_trans_realcomplexfft | ( | dsp32_complex_t * | vect1, |
| dsp32_t * | vect2, | ||
| int | nlog | ||
| ) |
32-bit fixed point version of the real to complex FFT algorithm.
| vect1 | A pointer on a 32-bit complex vector which is the output buffer of this function. |
| vect2 | A pointer on a 32-bit real vector which is the input buffer of this function. |
| nlog | It is the base-2-logarithm of the size of the input/output vector. Due to its implementation, this function computes only 4^n-point complex FFT. Therefore, the nlog argument has to be even. |
 1.8.5
1.8.5